Introduction:
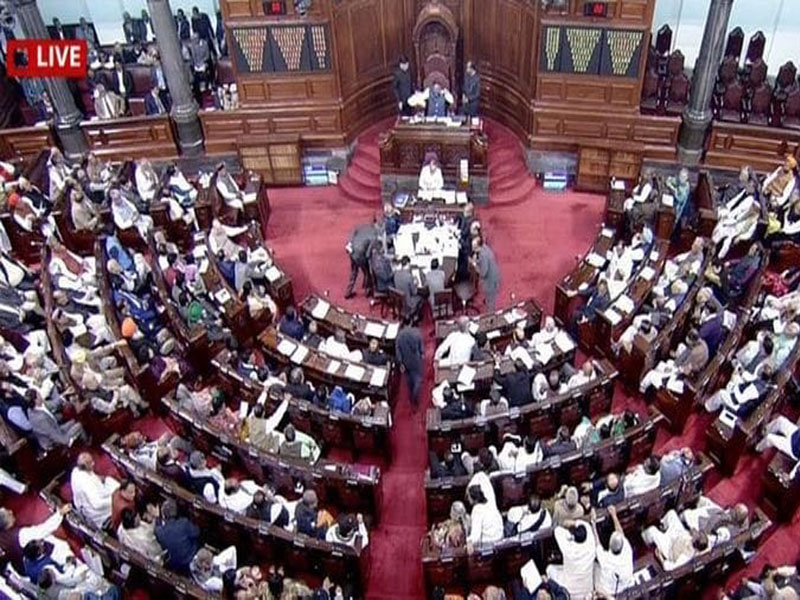
As we are aware of, our Indian Parliament is bicameral in nature meaning it has two houses operating i.e Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. Rajya Sabha is the upper house of the Parliament.
It is called the second chamber of the parliament and represents the states and union territories of the nation. It is built to protect the rights, interests and freedom of the states and union territories if the centre interferes in their work.
The Fourth Schedule of the Indian Constitution deals with allocation of seats in the Rajya Sabha.
Composition of Rajya Sabha:
Rajya Sabha has the maximum strength to have 250 members, where 238 members will have to represent States and Union Territories and 12 members have to be nominated by the President himself.
But now we have 245 members in Rajya Sabha with 13 vacancies. Here, 216 members represent the states and 4 members represent the union territories and 12 members are nominated by the president based on their contribution and expertise in the fields of: Art, Literature, Science, and Social Service
How are the Rajya Sabha members elected?
Rajya Sabha Members are elected by the elected members of state legislative assemblies. They use the method of proportional representation during the election process.
Can Rajya Sabha get dissolved?
Unlike Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha is a more permanent body. For, it does not dissolve after every five years. Rather, it continues and thus, termed as a ‘continuing chamber.’ In Fact, it keeps on running and never gets dissolved.
Only after every second year, one-third of its members retire. For the vacant seats, fresh elections take place.
Eligibilty of Rajya Sabha members:
- He/ She must be an Indian Citizen
- He/ She must be not less than 30 years of age
- He/ She must be registered as an elector for a parliamentary constituency.
Who is the head of Rajya Sabha?
Indian Vice-President presides over the chair of the Rajya Sabha, while there is also a deputy chairman of Rajya Sabha elected from among the members of the Rajya Sabha.
Both of them don’t have any voting rights until and unless there is a tie in the votes.
References:
https://byjus.com/free-ias-prep/upsc-mains-gs-paper-2-structure/#GS-2-Topics
Stay with
Prerna 🙂