In light of the current communal riots we are witnessing, it is important to know how Muslims became part of our nation and how for 4-5 centuries we have lived together in our motherland as brothers. Here are a few questions answered on the Mughal Dynasty.
Who founded the Mughal Dynasty?
The Mughal dynasty was founded by Babur. The dynasty is also called the Timurid dynasty as Babur was a descendant of Timur. Babur hailed from Ferghana (modern Uzbekistan), invaded northern India, and defeated Ibrahim Shah Lodi, the ruler of Delhi, in the first battle of Panipat in 1526. The Mughal Empire succeeded the Delhi Sultanate as rulers of northern India. In time, he conquered a major portion of India. The Mughal Empire dominated the Indian subcontinent between the mid-16th century and the early 18th century. Founded in 1526, it survived until 1858, when it was vanquished by the British.
How did Mugal architecture develop?
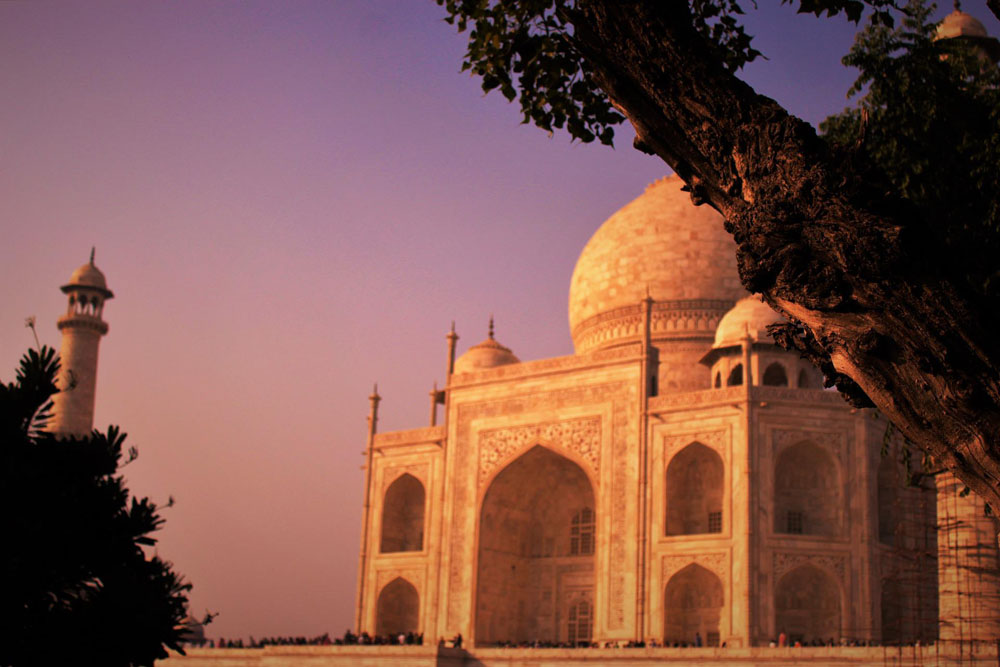
Mughal architecture- a mixture of Islamic, Persian, Turkish, and Indian architecture- was developed by the Mughals in the 16th and 17th centuries. Numerous forts, mosques, and palaces were built in this period. The Mughals built impressive tombs, including the beautiful tomb of Akbar’s father Humayun, and Akbar’s tomb at Sikandra, near Agra, which is a unique example of the architectural style of the Mughals. The Taj Mahal was built during the reign of the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal. The construction began around 1632 and was completed around 1653. More than 20,000 people were employed for construction and over 1000 elephants to transport building materials.
How was the Mugal empire administered?
Early Mughals like Babur and Humayun did not change the prevailing administration and style of ruling. However, Akbar adopted some rules of Sher Shah Suri’s administration but also introduced some new rules and practices. He established a strong and efficient administration. Equal rights were provided to Muslims and Non-Muslims and many Hindus were appointed to high positions in the Mughal administration. In Akbar’s rule, the emperor was the all-powerful sovereign head of the Mughal administration, who was assisted by a council of ministers. In contrast, Aurangzeb was known as a fundamentalist who enforced strict Islamic law on his empire. He ordered the destruction of Hindu temples, re-imposed jizya, and increased the land tax. This alienated the Hindus and led to many revolts.
Who were Akbar’s ‘Navratna’?
Akbar was a great patron of artists and intellectuals. His passion for knowledge attracted many great minds into his court. The best of his courtiers were known as the nine ‘jewels’ of King Akbar to ‘Navratnas’. Abul-Fazel was Akbar’s chief advisor and author of AKbarnama, Faizi was a poet laureate, Miyan Tansen was a legendary musician, Birbal was known for great wit, Raja Todar Mal was Akbar’s finance minister, Raja Man Singh was Akbar’s trusted general and Commander-in-chief, Adbul Rahim Khan-I-Khana was a poet and the son of Akbar’s trusted mentor, Bairam Khan. The mystic Fakir Aziao-Din and Mullah Do Piaza were both advisors to the Emperor.
Who built the Red fort in Delhi, India?
The Red Fort was built by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in Old Delhi that served as the capital of Mughal until 1857. For nearly 200 years, it was the center of Shah Jahan’s empire where he led a life known for great pomp and ceremony. He would make public appearances, called ‘darshan’, from a large balcony, receive public petitions in the Diwan-I-Am, review important state matters with his principal ministers in the Diwan-I-Khas, discuss the most secret affairs with his kin and the most trusted officers in the Royal Tower or Shah Burj, hold lively gatherings and feasts, and then retire to his bedchambers for the night. This fort was the greatest of Mughal palaces and was the heart of Shah Jahan’s empire.
Why was Akbar a great emperor?
The Mughal emperor Akbar came to power when he was just 13 years, following the death of his father Humayun. Akbar, under the mentor of his mentor Bairam Khan, expanded his territory throughout northern India and Afghanistan. Although he was not a great warrior, he was tolerant of other religions and was a very fair ruler. He succeeded in winning the trust and support of the entire Hindu population under his control. During his reign, he abolished two taxes: Jizya, a tax imposed on most non-Muslims, and a ‘pilgrimage tax’ paid by Hindus who traveled to various Hindu pilgrimage sites. He instituted any administrative reforms which were used throughout the Mughal period.
| Did you know that…
● The Mughal Emperor Aurangazeb used to play the musical instrument ‘veena’ perfectly? ● The reign of Shah-Jahn is called the ‘Golden Age of the Mughals? ● Babur wrote his memories called Tuzuk-i- Baburi in Turkish. ● The Taj Mahal appears pink in the morning, white during the day, and changes its color to golden in the moonlight.
|
Stay with
Prerna 🙂