🇮🇳 FACTS ABOUT INDIA 🇮🇳
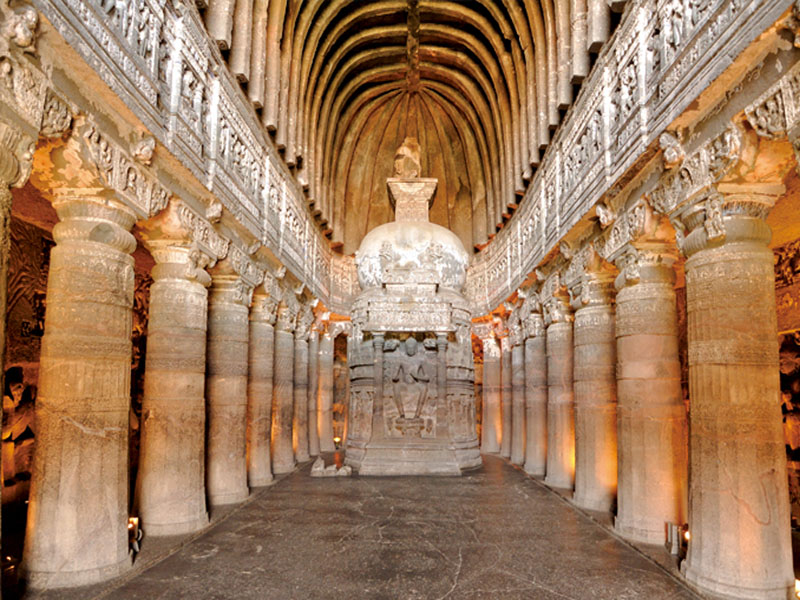
The Ajanta Caves are approximately 30 rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments which date from the 2nd century BCE to about 480 CE in Aurangabad district of Maharashtra state of India. The caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures described as among the finest surviving examples of ancient Indian art, particularly expressive paintings that present emotions through gesture, pose and form.
🛕 VEDIK GYAN
What is the significance of “Dhwaja Sthambam”(pole having many bells) in temples?
Dhwaja Stambha, or Flag Pole, is an important feature of most South Indian Temples. Dhwaja Stambha is installed in front of the temple.
Dhwaja Stambha is a tall post-like structure, which is referred to as the flag-mast of the deity of the temple. During festivities, the Dhwaja Stambha is decorated with different types of flags to commemorate and celebrate that particular event. The Dhwaja Stambha is present in a straight line from the deity, just before the Vahana of the deity, which is also in the same axial line.
Scientifically this was built to arrest the lightning- “Lightning arresting rod”
Whenever lightning strikes, the metal arrestor, placed such that it is the highest point of the region, induces the charge to conduct through it. The Arrestor then conducts the heavy electrical impulse directly to ground, thus preventing the building from getting damaged.
It can be noticed that the top of the Dhwaja Stambha is the highest point of the temple, and thus, whenever lightning would strike, the temple would be saved from the devastating damage that could have been caused.
This is what could be meant from the explanation that it connects “Heaven to earth” (i.e.) it conducts the charges from the clouds above during lightning to earth or ground, which is the electrical term for a no-potential area.
LEARN Sanskrit
यद् भावं तद् भवति
Yad bhavam tad bhavati
As you think so you become
*************
Click here to join:
https://t.me/joinchat/llGA9DGZF9xmMDc1
 |
Ms. Pooja, |