Chinese are world-renowned for exploiting the world for centuries. Here are a few stories we need to know about its past:
Who was the first emperor of China?
In 246 BC, the nine-year-old Zheng became the King of Qin (pronounced as ‘Chin’). In the next 35 years, he unified the seven quarreling kingdoms to make one kingdom, China. Thus, he became the first emperor of China. He called himself Qin Shi Huangdi. Before Qin Shi Huangdi, other great dynasties had also ruled, like the Shang or Zhou dynasties. During its reign, trade flourished, for instance, silk continued to be manufactured only in China for hundreds of years.
What is a dynasty?
Dynasties were not just found in China, but in different parts of the world, like the Windsor dynasty of Great Britain. A dynasty is a kind of succession to the throne. In general, a dynasty rules over a county for several generations. ‘In-house laws’ regulate- who succeeds to the throne in what sequence. Often they were only the male members of the family. The dynasty perished if there were no heirs to the throne. In China, the Qin dynasty was followed by many others. Under the Qing dynasty, China became the largest and the richest country by the end of the 18th century. The last Quing emperor abducted the throne in 1912.
How did Qin Shi Huangdi unite China?
The emperor passed uniform laws. He put together the different parts of the seven quarreling kingdoms to make a single script with over 3000 characters. He also ensured that at all places the same weights and coins were valid. The same wheel distance of carriages made it easy to build roads and simplified trade in the entire kingdom. The emperor got roads made from the capital city to each part of the country including a straight 900 km long road to the north.
Why was the terracotta army made?
The Chinese also believed in life after death just like the Egyptians. So they laid food, weapons, and jewelry along with rulers in the graves. The Shang dynasty believed that people should also follow the king to the other side and servants were often laid in the same grave. However, since the Zhou dynasty, only figures of guards were laid in the graves. Such a life-sized figure made of terracotta and unglazed clay was discovered accidentally by farmers in 1974 while they were digging for water near the grave of the first emperor. Till now archeologists have discovered more than 8000 figures. It is assumed that 3 people worked for 15 days to make one terracotta soldier.
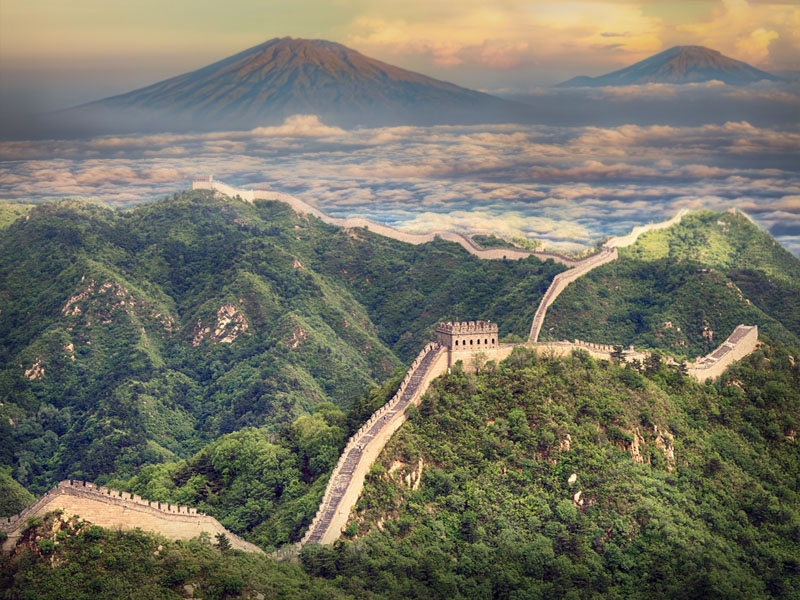
When was the Great Wall of China built?
The Great Wall of China was built over 2000 years ago by Qin Shi Huangdi, the first emperor of China, during the Qin (Ch’in) Dynasty (221 BC-206 BC). He got a 6000 km long, 8 m high, and 5-6 m wide wall built along the borders of his kingdom in just seven years. The wall was made from the materials available at those times, which were sand, gravel, wood, and stones brought from mountains. Hundreds of thousands of people worked to build the wall under the threat of being punished. It is believed that probably more than a million workers died during its construction. The wall protected China against attacks from other countries.
How is silk made?
The production of silk is very cumbersome. The silkworm gives the fibers for making silk. This is the larva of the silk spider, a kind of butterfly. The larvae were fed mulberry leaves. When the larvae change into pupas, they make fiber from a thick liquid in their mouth, which they wind around themselves a thousand times. These cocoons are killed in hot water and the silk fiber is rolled out very carefully. About 7-9 kg of cocoons are killed for 1 kg of raw silk. China kept the knowledge of breeding silkworms and the manufacture of silk secret for many centuries. The first silk came to Europe at the birth of Christ, and it was sold at a very high price. The valuable product was traded via the Mediterranean Sea through the silk route, a secure trade route.
| Did you know that…
● Persian monks smuggled silkworms and mulberry seeds to Europe in the 6th century AD as economic spies? ● Jade, a greenish gemstone, was more valuable to the Chinese than gold. ● The famous Mongolian ruler Genghis Khan overcame the Great Wall of China in 1210 with 100,000 soldiers and conquered Peking, the capital city of China. |
Stay with
Prerna 🙂